THP1-Dual™ KI-mSTING Cells
-
Cat.code:
thpd-mstg
- Documents
ABOUT
Murine STING knockin dual reporter monocytes
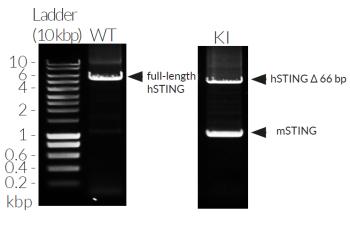
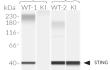
THP1-Dual™ KI-mSTING cells stably express the wild-type murine STING (stimulator of interferon genes, mSTING also known as TMEM173) gene. They were generated by knockin (KI) of the mSTING intronless coding sequence (from ATG to TGA) into THP1-Dual™ KO-STING cells, which derive from the human THP-1 monocytes.
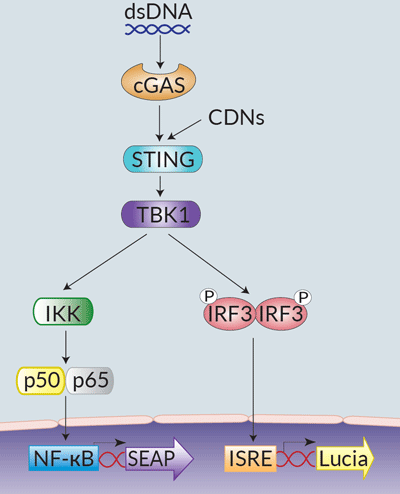
STING is a cytosolic pattern recognition receptor (PRR) that acts as a direct sensor of cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) [1]. The binding of CDNs to STING leads to TANK-binding-kinase-I (TBK1)-mediated interferon regulatory factor (IRF3) activation and type I interferon (IFN) production [1] and to NF-κB-dependent inflammatory cytokine production [2].
THP1-Dual™ KI-mSTING cells feature two reporter genes allowing the simultaneous study of the IRF pathway, by monitoring the activity of an inducible secreted Lucia luciferase, and the NF-κB pathway by monitoring the activity of an inducible SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase). Lucia luciferase and SEAP activities are readily assessable in the supernatant using QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia and QUANTI-Blue™ Solution detection reagents, respectively.
As expected, THP1-Dual™ KI-mSTING cells exhibit a robust response to STING agonists such as 2’3’-cGAMP and 3’3’-cGAMP. In addition, these cells respond to DMXAA (5,6-Dimethylxanthenone 4-acetic acid), a potent activator of murine STING-dependent IFN responses, that does not activate human STING [3]. These cells are resistant to Blasticidin and Zeocin™.
Features of THP1-Dual™ KI-mSTING Cells:
- Knockin of the mSTING gene
- No functional hSTING expression
- IRF activation readily assessable using the Lucia luciferase reporter gene
- NF-κB activation readily assessable using the SEAP reporter gene
Validation of THP1-Dual™ KI-mSTING Cells:
- Murine STING knockin verified by PCR, DNA sequencing, and Western blot
- Functionally tested
References:
1. Sun L. et al., 2013. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science. 339:786-91.
2. Ishikawa H. & Barber G.N. 2008. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 455:674-8.
3. Zhang H. et al., 2015. Rat and human STINGs profile similarly towards anticancer/antiviral compounds. Sci Rep. 5:18035.
Disclaimer: These cells are for internal research use only and are covered by a Limited Use License (See Terms and Conditions). Additional rights may be available.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
STING
Mouse
Dual reporter assays for mSTING pathway, NF-κB and IRF signaling pathways
Complete RPMI 1640 (see TDS)
Verified using PlasmotestTM
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:THP1-Dual™ KI-mSTING Cells
-
Cat code:thpd-mstg
-
Quantity:3-7 x 10^6 cells
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution)
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Dry ice
- Liquid nitrogen vapor
- Upon receipt, store immediately in liquid nitrogen vapor. Do not store cell vials at -80°C.
Storage:
Caution:
Details
STING (stimulator of interferon genes; also known as TMEM173, MITA, MPYS, and ERIS) is essential for the interferon (IFN) response to microbial or self-DNA, and acts as a direct sensor of cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs). CDNs are important messengers in bacteria and innate immune agonists in mammals.
Upon bacterial infection, CDNs released into cells bind directly to STING leading to TANK-binding-kinase-I (TBK1)-mediated IFN regulatory factor (IRF3) activation and type I IFN production. Distinct variants of human STING (hSTING) that affect CDN recognition and signal transduction have been identified.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?