HCT116-Dual™ Cells
-
Cat.code:
hctd-nfis
- Documents
ABOUT
Human HCT116 colorectal carcinoma - NF-κB & IRF reporter cells
HCT116-Dual™ cells are adherent epithelial cells that have been derived from the human HCT116 colorectal carcinoma cell line by stable integration of two inducible reporter constructs.
HCT116-Dual™ cells express a secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter gene under the control of the IL-12 p40 minimal promoter fused to five NF-κB and AP-1 binding sites.
HCT116-Dual™ cells also express the Lucia luciferase gene, which encodes a secreted luciferase, under the control of an ISG54 minimal promoter in conjunction with five IFN-stimulated response elements.
As a result, HCT116-Dual™ cells allow to simultaneously study the NF-κB pathway, by assessing the activity of SEAP, and the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) pathway, by monitoring the activity of Lucia luciferase.
Both reporter proteins are readily measurable in the cell culture supernatant when using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent, and QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Lucia/Gaussia, a Lucia and Gaussia luciferase detection reagent.
Disclaimer: These cells are for internal research use only and are covered by a Limited Use License (See Terms and Conditions). Additional rights may be available.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
Screening of PRR agonists or inhibitors
Complete DMEM (see TDS)
Verified using Plasmotest™
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:HCT116-Dual™ Cells
-
Cat code:hctd-nfis
-
Quantity:3-7 x 10^6 cells
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
- 1 tube of QUANTI-Luc™ 4 Reagent, a Lucia luciferase detection reagent (sufficient to prepare 25 ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Dry ice
- Liquid nitrogen vapor
- Upon receipt, store immediately in liquid nitrogen vapor. Do not store cell vials at -80°C.
Storage:
Caution:
Details
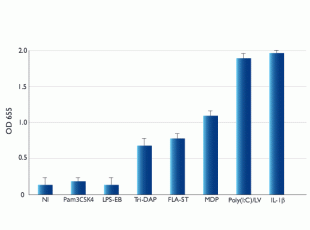
HCT116-Dual™ cells express numerous pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), including the NOD-like receptors (NLRs) NOD1 and NOD2 [1, 2], the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) RIG-I [3, 4], and the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) TLR3 and TLR5 [5] but not TLR2 or TLR4 [2].
Upon recognition of their cognate PAMPs, these receptors induce signaling pathways leading to the activation of the transcription factors NF-kB and/or IRF3/7. Stimulation of HCT116-Dual™ cells with the following PAMPs: Poly(I:C) (TLR3), flagellin (TLR5), Tri-DAP (NOD1), and MDP (NOD2), leads to the activation of NF-kB. Stimulation with RLR ligands, such as transfected poly(I:C) or poly(dA:dT), or the STING agonist, 2’3’-cGAMP, triggers the IRF pathway.
Stimulation with RLR ligands, such as transfected poly(I:C) or poly(dA:dT), or the STING agonist, 2’3’-cGAMP, triggers the IRF pathway.
HCT116-Dual™ cells are resistant to the selectable markers blasticidin and Zeocin™.
1. Rickard DJ. et al., 2014. Identification of selective small molecule inhibitors of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1 (NOD1) signaling pathway. PLoS One. 9(5):e96737.
2. Zhao L. et al., 2007. Differential modulation of Nods signaling pathways by fatty acids in human colonic epithelial HCT116 cells. J Biol Chem. 282(16):11618-28.
3 Gack MU. et al., 2008. Roles of RIG-I N-terminal tandem CARD and splice variant in TRIM25-mediated antiviral signal transduction. PNAS. 105(43):16743-8.
4. Taura M. et al., 2008. p53 regulates Toll-like receptor 3 expression and function in human epithelial cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 28(21):6557-67.
5. Klimosch SN. et al., 2013. Functional TLR5 genetic variants affect human colorectal cancer survival. Cancer Res. 73(24):7232-42.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?