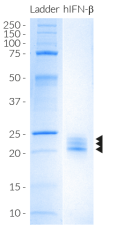
Recombinant human IFN-β
-
Cat.code:
rcyc-hifnbNEW
- Documents
ABOUT
Human IFN-β protein - Mammalian cell-expressed, tag-free, carrier-free
Recombinant human IFN-β is a high-quality and biologically active cytokine, validated using proprietary IFN-α/β reporter cells. This member of the type I interferon family is produced in CHO cells to ensure protein glycosylation and bona fide 3D structure.
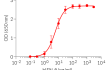
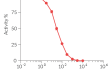
Recombinant human IFN-β can be used together with HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells for screening molecules that inhibit IFN-β signaling, such as Anifrolumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the IFNAR subunits of the IFN-β receptor (see figures).
Key features
- Each lot is validated using HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells
- Endotoxin ≤ 1 EU/µg
- 0.22 µm sterile-filtered
Applications
- Standard for IFN-β detection and quantification assays
- Screening and release assays for antibodies blocking IFN-β signaling
- Screening and release assays for engineered IFN-β
Interferon beta (IFN-β) is an important member of the type I IFN family. It is an important anti-viral cytokine that also plays anti-proliferative and immunomodulatory roles.
All InvivoGen products are for internal research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
P01574
>108 IU/mg*
100 μg/ml in water
10 mM Sodium Acetate (pH 4.5), 5% trehalose, 5% mannatol, and 0.01% Tween-80
0.22 µm filtration
The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK‑Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Cellular assays (tested), ELISA
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
*Please refer to the corresponding Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for the exact value.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:Recombinant human IFN-β
-
Cat code:rcyc-hifnb
-
Quantity:20 µg
1.5 ml endotoxin-free water
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Room temperature
- -20°C
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
Storage:
Caution:
Details
IFN-β background
IFN-β belongs to the type I interferon (IFN) family. IFN-β and IFN-α are the most broadly expressed type I IFNs. They are important anti-viral cytokines that also play anti-proliferative and immunomodulatory roles [1, 2].
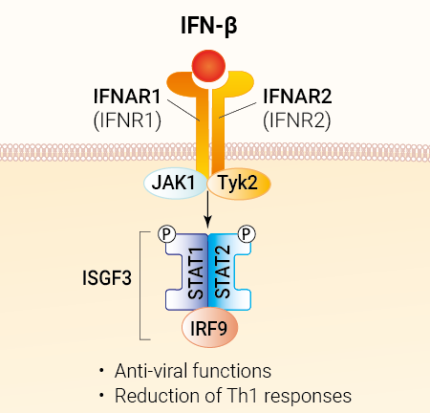
IFN-β and all of the IFN-α subtypes bind to a heterodimeric transmembrane receptor composed of the subunits IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, which are associated with the tyrosine kinases Tyk2 and Jak1 (Janus kinase 1), respectively. These kinases phosphorylate STAT1 and STAT2, which then dimerize and interact with IFN regulatory factor 9 (IRF9), leading to the formation of the ISGF3 complex. ISGF3 binds to IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE) in the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG) to regulate their expression.
Relevance for therapeutics development
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a multifactorial chronic demyelinating disease that causes serious damage in the central nervous system. There is increasing evidence that Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) infection is involved in the disease processes [2]. IFN-β therapies are a major class of drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat relapsing/remitting MS. These include recombinant human IFN-β1a (e.g., Rebif), pegylated IFN-β1a (Plegridy), and recombinant human IFN-β1b (e.g., Betaferon). Although their mode of action is not fully elucidated, IFN-β therapies could counterweigh the EBV signature at multiple points by sustaining EBV-specific B cell responses and reducing the number of circulating EBV-specific CD8+ T cells to restrain excessive and damaging lytic responses [2].
Despite their protective effects, studies have shown that aberrant expression of the type I IFNs can elicit autoimmune disorders, such as interferonopathies and SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus). Recent evidence also implicates type I IFN-dependent signaling as a key inflammatory driver in non-autoimmune diseases [3].
Anifrolumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the type I IFN receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR1) and blocks the type I IFN signaling. It is approved by the FDA as an add-on therapy for moderately to severely active SLE [4].
References:
1. McNab, F., et al., 2015. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 15(2):87-103.
2. Belluci., G., et al., 2023. The value of Interferon β in multiple sclerosis and novel opportunities for its anti-viral activity: a narrative literature review. Front Immunol. 14:1161849.
3. Crow MK, Ronnblom L., 2019. Type I interferons in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Lupus Sci Med. 6(1):e000336.
4. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Report). 2022. Advancing Health Through Innovation: New Drug Therapy Approvals 2021.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?