HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β Cells
-
With a free vial of human IFN-α2b protein
-
Cat.code:
hkb-ifnabv2-a
- Documents
ABOUT
IFN-α/β responsive ISGF3-SEAP reporter assay
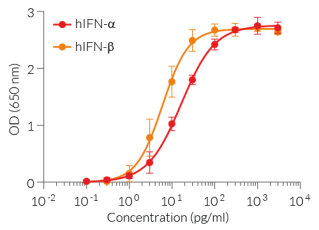
HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells* are designed to monitor human IFN-α and IFN-β-induced ISGF3 stimulation or inhibition. This colorimetric bioassay can be used for screening activatory molecules, such as engineered cytokines, or inhibitory molecules, such as neutralizing antibodies.
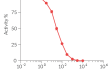
HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells respond specifically to recombinant human IFN-α and human IFN-β. The reliable and consistent performance of HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells makes them suitable for release assays of therapeutic molecules that inhibit IFN-α signaling, such as Rontalizumab and Aniftrolumab, two monoclonal antibodies targeting IFN-α and its receptor, respectively (see figures).
Key features
- Readily assessable ISGF3-SEAP reporter activity
- Convenient readout using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution
- High sensitivity to human (h)IFN-α and IFN-β activity
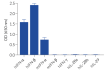
- Poor to no response to mouse (m)IFN-α and mIFN-β
- No response to hIFN-γ and hIFN-λs (IL-28a, IL-28b, and IL-29)
- Stability guaranteed for 20 passages
Applications
- Therapeutic development
- Drug screening
- Release assay
Type I interferons, in particular interferon alpha (IFN-α) and interferon beta (IFN-β), are important anti-viral cytokines that also play anti-proliferative and immunomodulatory roles.
* Note: A new clone is provided with an improved Type I IFN response. The cat code has been changed accordingly (hkb-ifnabv2).
Disclaimer: These cells are for internal research use only and are covered by a Limited Use License (See Terms and Conditions). Additional rights may be available.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
IFN-α, IFN-β
Human
Detection and quantification of IFN-α and IFN-β activity
10 pg/ml - 3 ng/ml (hIFN-α2b)
3 pg/ml - 3 ng/ml (hIFN-β)
Complete DMEM (see TDS)
Verified using Plasmotest™
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β Cells
-
Cat code:hkb-ifnabv2-a
-
Quantity:3-7 x 10^6 cells
- 1 ml of Blasticidin (10 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Zeocin® (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml Normocin® (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent)
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Dry ice
- Liquid nitrogen vapor
- Upon receipt, store immediately in liquid nitrogen vapor. Do not store cell vials at -80°C.
Storage:
Caution:
Details
Cell line description
HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells were generated by stable transfection with the genes encoding human STAT2 and IRF9 to obtain a fully active type I interferon (IFN) signaling pathway. The other genes of the pathway (IFNAR1, IFNAR2, JAK1, TyK2, and STAT1) are naturally expressed by these cells. HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells were also stably transfected with the secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter under the control of the ISG54 promoter. This promoter comprises IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE) that are recognized by the ISGF3 complex. The binding of IFN-α or IFN-β to their receptor triggers a signaling cascade leading to the activation of ISGF3 and the subsequent production of SEAP. This can be readily assessed in the supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells detect human (h) IFN-α and hIFN-β. At high concentrations, they might respond to mouse (m) IFN-α, but not mIFN-β. Of note, HEK-Blue™ IFN-α/β cells do not respond to human type II (IFN-γ) and type III IFNs (IFN-λs: IL-28a, IL-28b, and IL-29) (see figures).
IFN-α and IFN-β background
Type I interferons, in particular interferon-alpha (IFN-α) and interferon beta (IFN-β), play a vital role in host resistance to viral infections [1, 2]. The type I IFN family is a multi-gene cytokine family that encodes 13 partially homologous IFN-α subtypes in humans (14 in mice), a single IFN-β, and several poorly defined single-gene products (IFN-ɛ, IFN-τ, IFN-κ, IFN-ω, IFN-δ, and IFN-ζ) [1, 2]. IFN-α and IFN-β are the best-defined and most broadly expressed type I IFNs [2].
IFN-β and all of the IFN-α subtypes bind to a heterodimeric transmembrane receptor composed of the subunits IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, which are associated with the tyrosine kinases Tyk2 and Jak1 (Janus kinase 1), respectively. These kinases phosphorylate STAT1 and STAT2 , which then dimerize and interact with IFN regulatory factor 9 (IRF9), leading to the formation of the ISGF3 complex. ISGF3 binds to IFN-stimulated response elements (ISRE) in the promoters of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG) to regulate their expression.
Relevance for therapeutic development
Despite their protective effects, studies have shown that aberrantly expression of the type I IFN system can elicit autoimmune disorders, such as interferonopathies and SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus). Recent evidence also implicates type I IFN-dependent signaling as a key inflammatory driver in non-autoimmune diseases [3].
Rontalizumab (aka rhuMAb interferon-alpha) is a therapeutic, humanized monoclonal antibody (mAb) that targets the human interferon-alpha (IFN-α) cytokine subtypes [4, 5]. By binding to IFN-α, Rontalizumab prevents it from interacting with its receptor (IFNAR) on the surface of immune cells, thus inhibiting the downstream inflammatory response. Rontalizumab has been clinically evaluated as an immunosuppressive agent for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [4-6].
Anifrolumab is a fully human mAb designed to target the type I IFN receptor subunit 1 (IFNAR1) and to block the type I IFN signaling. Anifrolumab features a triple mutation L234F/L235E/P331S in the heavy chain to reduce engagement with the cell surface Fc gamma receptor (FcγR) and potential Fc-mediated effector function, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) [7-8]. According to the FDA, it is a first-in-class medication highlighting its innovative and unique mechanism of action [9]. It has been approved as an add-on therapy for moderately to severely active SLE [9].
References:
1. Schreiber G. 2017. The molecular basis for differential type I interferon signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 292:7285-94.
2. McNab F. et al., 2015. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 15(2):87-103.
3. Crow MK, Ronnblom L., 2019. Type I interferons in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Lupus Sci Med. 6(1):e000336.
4. McBride JM, et al. 2012. Safety and pharmacodynamics of rontalizumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a phase I, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-escalation study. Arthritis Rheum. 64(11):3666-76.
5. Kalunian KC, et al., 2016. A Phase II study of the efficacy and safety of rontalizumab (rhuMAb interferon-alpha) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (ROSE). Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:196–202.
6. Jones, S.A. and Morand, E.F., 2024. Targeting Interferon Signalling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Lessons Learned. Drugs. 84(6):625-635.
7. Plüß M, et al., 2022. Rapid Response of Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Skin Manifestations to Anifrolumab-A Case-Based Review of Clinical Trial Data Suggesting a Domain-Based Therapeutic Approach. J Clin Med. 11(12):3449.
8. Riggs JM, et al., 2018. Characterization of anifrolumab, a fully human anti-interferon receptor antagonist antibody for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci Med. 5(1):e000261.
9. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Report). 2022. Advancing Health Through Innovation: New Drug Therapy Approvals 2021.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?
You may also need
FAQ
HEK293 cell line description
In the United States, HEK293 cell lines are designated Biosafety Level 2 according to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
In Germany, HEK293 cell lines are designated Biosafety Level 1 according to the Central Committee of Biological Safety, Zentrale Kommission für die Biologische Sicherheit (ZKBS).
You can check with your country’s regulatory authority regarding the use of these cells.
Please note that there is no replicating/infectious Adenovirus 5 in these cells.
The minimal promoter isn't the same but the difference in expression for these two Null cell lines is minor.
There is no specific integration system used to generate our stable cell lines.
The selection pressure is enough to obtain stable clones. The receptors are added by simple transfection of plasmids using a cationic lipidic transfection agent (the plasmids are not linearized before transfection).
Only our HEK-Blue™ Null1-k and Null2-k cells are sensitive to G418.
The only HEK-Blue™ Null cells that are sensitive to Puromycin are the HEK-Blue™ Null1-v cells.
The only HEK-Blue™ Null cells that are sensitive to Puromycin are the HEK-Blue™ Null1-v cells.
Our RNAseq data confirms that our HEK-Blue™ cells express FcRN, however, this has not been functionally tested.
The difference in activity is approximately 10-fold.
Both cell types overexpress a designated TLR. The primary difference is that HEK-Blue™ cells include the NFκB inducible SEAP reporter construct.
We presume them to be in the endosome as we express the wild-type, full-length genes. Additionally, their signal can be blocked by Chloroquine, an endosomal acidification inhibitor. However, as these TLRs are over-expressed there may potentially be low expression of them on the cell surface.
HEK-Blue™ cells only express a single NFκB inducible SEAP reporter gene. Whereas, HEK-Dual™ cells have the addition of the Lucia™ gene knocked into the IL-8 locus. Thus, when IL-8 is activated following stimulation, HEK-Dual™ cells can report this with the secretion of Lucia™ luciferase.
It should also be noted that the HEK-Dual™ cells have been knocked out for TLR3, TLR5, and TNFR to limit interference from other TLRs when studying a specific TLR pathway.
HEK293 cells express TLR1, TLR3, TLR5, TLR6, and NOD1.
They respond to TLR3, TLR5, and NOD1 agonists, but at a much lower level compared to HEK293 cells transfected with these receptors
HEK-Blue™ IL-1R cells express both human and murine IL-1β receptors, thus can detect both species.
On the other hand, HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells are specific for human IL-1β, but can still detect higher concentrations of mouse IL-1β.
Cell line culture
The split ratio will depend on when you expect confluency. Typically, the doubling time of HEK-Blue™ cells is approximately 24 hours.
Therefore, if you use a split ratio of 1:2 (50%) into a new flask, cells should be confluent the following day. If you use a split ratio of 1:4 (25%) you can expect the cells to be confluent after 2 days.
Our HEK-Blue™ Selection is provided in 1ml tubes with each containing a 250X solution.
Therefore, you should dilute HEK-Blue™ Selection 1:250 into your media to have a 1X concentration.
HEK-Blue™ cells should be seeded at a density of approximately 1.5 x 106 cells in a T25 flask or 4 – 5 x 106 cells in a T75 flask.
We recommend using a flat-bottom, clear walled cell culture plate.
Below are a few tips we recommend to help get your HEK cells growing:
• For the first 2-3 passages, grow cells in media containing 20% FBS and no antibiotics.
• Do not allow cells to reach 100% confluency Please check cells as regularly as possible.
• The cells should not be grown in 20% FBS for too long. Use media with 10% FBS after 2 or 3 passages.
• When making frozen stocks, continue growing additional cultures in case there is a problem with the frozen stock.
Trypsin does not adversely affect the health or growth of these cells. However, it is known that high concentrations will occasionally induce the activation of NFκB resulting in a higher background in your assay.
Moreover, we have observed some cases where trypsin has been contaminated with TLR2, TLR4, and TLR5 contaminants, which can also interfere with the assay results.
It is not unusual for different TLR cells to grow at different rates. Some TLR clones happen to grow a little slower/faster than others. This is often clone dependent.
When the HEK-Blue™ cells are non-adherent, either they were diluted too harshly at the start or they have grown over-confluent in a small flask and suffocated.
To avoid this in the future:
• Change the media and plate the cells at a density of approximately 1.5 x 106 cells in a T25 flask.
• Wash the cells before putting them into a new flask. Sometimes when the cells are non-adherent, it is due to the clustering of both live and dead cells. Additionally, this will get rid of any remaining DMSO which could affect the adhesion of the cells to the flask.
• Use medium with 20% FBS.
• The use of CellBIND flasks can sometimes help to increase attachment and growth of the cells (however CellBIND flasks are not required in the normal protocol).
Assays
We recommend to not use any antibiotics at all during assays to ensure the least amount of potential interfering agents in the medium.
Therefore, we do not add HEK-Blue™ Selection to the test media.
We have only tested the use of plasma and serum samples on our HEK-Blue™ hTLR2 cell line.
The results demonstrated that when compared to using standard samples (in DMEM), serum samples give a single log difference.
On the other hand, we found a 3-log difference between DMEM and plasma samples.
This is why we would recommend using serum samples over plasma samples.
Yes, they can be used interchangeably. However, please note that the protocols are distinctly different and need to be followed accordingly.
HEK293 cells are very easy to transfect with a transfection efficiency of approximately 80%.
It depends on the cell line and the concentration of the ligand used to stimulate the cells. In general, we record the results following 16 – 24 hours of stimulation.
There are 2 possible explanations as to why a blue color is observed in all wells.
1. It could be due to the presence of Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) in the culture medium. To see if this is the case, there is a very simple test to perform. Add 50 µl of the medium used for cell culture (without cells) and 200 µl of resuspended HEK-Blue™ detection medium or QUANTI-Blue™. If the medium turns blue, then it is due to the presence of Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) in the serum of the media. In this case, you must heat the serum to inactivate the AP and repeat the medium test. At this point the test should give a negative result (no blue color).
2. It could be due to improper handling of cells before the test. To avoid activation of NFκB before stimulation and reduce the risk of false positive results:
• Use pre-warmed PBS to wash cells
• Use heat-inactivated FBS
• Do not centrifuge cells prior to stimulation
• Do not use trypsin
We have noticed a loss of sensitivity when using HEK-Blue™ Detection medium instead of QUANTI-Blue™ on our cytokine reporter cell lines.
Therefore, we recommend using QUANTI-Blue™, which is provided with the cells, as this is what we use in house.