HEK-Blue™ IL-25/IL-17C Cells
-
Cat.code:
hkb-il17c
- Documents
ABOUT
IL-25 (IL-17E) and IL-17C responsive NF-κB/AP-1-SEAP reporter assay
HEK-Blue™ IL-25/IL-17C cells are designed to monitor IL-25 and IL-17C-induced NF-κB/AP-1 stimulation or inhibition. This colorimetric bioassay can be used for screening activatory molecules, such as engineered cytokines, or inhibitory molecules, such as neutralizing antibodies.
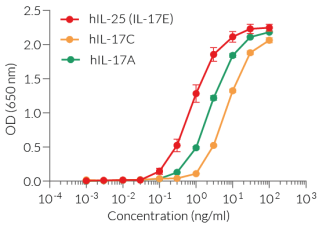
HEK-Blue™ IL-25/IL-17C reporter cells respond to recombinant human IL-25 (also known as IL-17E) and to its mouse counterpart. These cells also detect human (h) IL-17C, mouse (m) IL-17C, and hIL-17A. They display little to no response to hIL-17F and do not respond to mIL-17A nor mIL-17F (see figures). Of note, HEK-Blue™ IL-25/IL-17C cells do not respond to hIL-17B nor hIL-17D (data not shown). The reliable and consistent performance of HEK-Blue™ IL-25/IL-17C cells makes them suitable for release assays of therapeutic molecules that inhibit IL-17/IL-25 signaling.
Key features
- Readily assessable NF-κB/AP-1-SEAP reporter activity
- Convenient readout using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution
- Strong response to human (h) and mouse (m) IL-25 (IL-17E) & IL-17C
- Moderate response to hIL-17A
- Low to no response to mIL-17A & h/mIL-17F
- Stability guaranteed for 20 passages
Applications
- Therapeutic development
- Drug screening
- Release assay
The interleukin-17 (IL-17) family comprises six members (IL-17A – 17F), which have various biological functions, including driving an inflammatory cascade during infections and autoimmune diseases. IL-25 is mainly produced by epithelial cells and promotes the expression of type 2 cytokines in barrier tissues (e.g., skin, lungs, gastrointestinal tract). IL-17C is a pro‑inflammatory cytokine that promotes Th17 immunity to pathogens in the lungs, skin, and colon.
Disclaimer: These cells are for internal research use only and are covered by a Limited Use License (See Terms and Conditions). Additional rights may be available.
InvivoGen also offers
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
IL-17C, IL-25 (IL-17E), IL-17A
Human, Mouse
Detection and quantification of IL-17/IL-25 activity
3 - 100 ng/ml (hIL-17C, mIL-17C)
0.3 - 100 ng/ml (hIL-25 (hIL-17E), mIL-25 (mIL-17E)
10 - 100 ng/ml (hIL-17A)
Complete DMEM (see TDS)
Verified using Plasmotest™
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:HEK-Blue™ IL-25/IL-17C Cells
-
Cat code:hkb-il17c
-
Quantity:3-7 x 10^6 cells
- 2 x 1 ml of HEK-Blue Selection (250X concentrate)
- 1 ml of Normocin® (50 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of QB reagent and 1 ml of QB buffer (sufficient to prepare 100 ml of QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent).
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Dry ice
- Liquid nitrogen vapor
- Upon receipt, store immediately in liquid nitrogen vapor. Do not store cell vials at -80°C.
Storage:
Caution:
Details
Cell line description
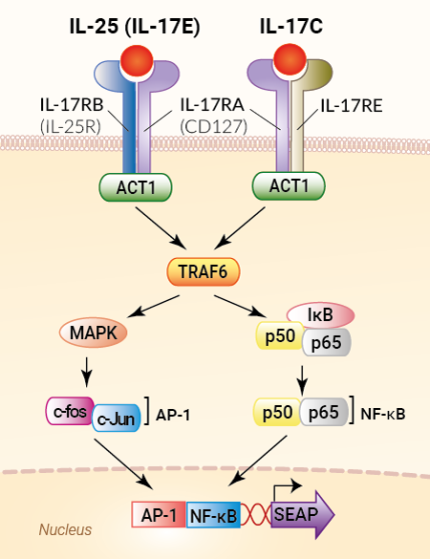
HEK-Blue™ IL-17C cells were generated from the human embryonic kidney HEK293 cell line by the stable transfection with the genes encoding for the human IL-17C receptor (IL-17RA and IL-17RE chains), the ACT1 adaptor molecule, as well as an NF-κB- and AP-1-inducible secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) reporter. The binding of IL-17C to its receptor triggers a signaling cascade leading to the activation of NF-κB/AP-1 and the subsequent production of SEAP. This can be readily assessed in the supernatant using QUANTI-Blue™ Solution, a SEAP detection reagent.
Interleukin-17 background
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) is a family of six closely related cytokines (IL-17A to IL-17F) that can have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory activities. IL-17C is a pro‑inflammatory cytokine that promotes Th17 immunity to pathogens in the lungs, skin, and colon [1].
IL-17 cytokines exert their biological activities following binding to heterodimeric receptors containing the ubiquitous IL-17RA chain and a second IL-17R (C, B, or E) chain. IL-17A and IL-17F bind to the IL-17RA/IL-17RC receptor, IL-17C binds to the IL-17RA/IL-17RE receptor, and IL-17E binds to the IL-17RA/IL-17RB receptor [1, 2]. The activated heterodimeric receptor recruits the Act1 adaptor and induces the TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) ubiquitylation. This triggers a signaling cascade that results in NF-κB and AP-1 activation [3].
References:
1. Yamaguchi S. et al., 2018. The roles of IL-17C in T cell-dependent and -independent inflammatory diseases. Sci Rep. 8(1):15750.
2. Gu C. et al., 2013. IL-17 family: cytokines, receptors and signaling. Cytokine. 64(2):477-85.
3. Pappu R. et al., 2011. The interleukin-17 cytokine family: critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Immunology. 134(1): 8–16.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?