NT-0796
-
Cat.code:
inh-nt0796
- Documents
ABOUT
NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor
NT-0796 is an orally active, selective, fully brain-penetrant inhibitor of the NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3, cryopyrin, or NALP3) inflammasome [1-4]. It is currently being tested in clinical trials for its potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases (e.g. Parkinson's) and chronic inflammation in obesity [1,2]. The multiprotein NLRP3 inflammasome complex is a key player in innate immune responses [4].
Mode of action
The NT-0796 is an ester pro-drug of the carboxylic acid active species NDT-19795 [1]. NT-0796 gets metabolized by carboxylesterase-1 (CES1) in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to yield the active metabolite NDT-19795, which finally binds and inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome [4]. Recent studies revealed that NTD-19795 binds to the NACHT domain of NLRP3, preventing the conformational changes required for inflammasome activation [1,3].
As mentioned above, CES1 is required to convert NT-0796 to the active pharmacophore NDT-19795 [1,3,4]. CES1 is abundantly expressed in the liver, as well as in human monocytes and macrophages (e.g. THP-1 cells). However, it is not found in mouse macrophages or other human cell types, such as HEK 293 and HepG2 cells. This makes study design more complex and requires humanized mouse models that express human CES1 (hCES1) [4].
However, carboxylate esterification has many advantages since it improves bioavailability, facilitates passage across membrane barriers, and enhances tissue distribution of small molecule therapeutics [4]. Moreover, NT-0796 was shown to be >100-fold more potent than NDT-19795 at inhibiting the same cellular responses. This difference in potency is attributed to neutral NT-0796 being taken up by the cells more readily than negatively charged NDT-19795 [4].
Overall, NT-0796 has proved to be a promising, orally administrable therapeutic NLRP3 inhibitor with demonstrated in vivo CNS brain penetration [1]. InvivoGen's NT-0796 specifically inhibits NLRP3-dependent cell death, as verified using the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay. Moreover, it successfully blocks the release of IL‑1β induced by NLRP3 activators, such as MSU or CPPD crystals, assessed using InvivoGen's THP-1 / HEK-Blue™ IL-1β release assay (see figures).
Key features
- A potent and specific inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome
- InvitroFit™ grade: each lot is highly pure (≥95%) and functionally tested
![]() Read our review on the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Read our review on the NLRP3 inflammasome.
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes.
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes.
References:
1. Harrison D, et al., 2023. Discovery of Clinical Candidate NT-0796, a Brain-Penetrant and Highly Potent NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor for Neuroinflammatory Disorders. J Med Chem. 9;66(21):14897-14911.
2. Thornton P, et al., 2024. Reversal of High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity, Systemic Inflammation, and Astrogliosis by the NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitors NT-0249 and NT-0796. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.;388(3):813-826
3. Doedens JR, et al. 2024. The ester-containing prodrug NT-0796 enhances delivery of the NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor NDT-19795 to monocytic cells expressing carboxylesterase-1. Biochem Pharmacol. ;227:116455.
4. Smolak P, et al., 2024. Target cell activation of a structurally novel NLRP3 inhibitor NT-0796 enhances potency. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics January 22, 2024, JPET-AR-2023-001941;
All products are for research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
InvitroFit™
InvitroFit™ is a high-quality standard specifically adapted for in vitro studies of inhibitors. InvitroFit™ products are highly pure (≥95%) and guaranteed free of bacterial contamination, as confirmed using HEK Blue™ TLR2 and HEK Blue™ TLR4 cellular assays. Each lot is rigorously tested for functional activity using validated (or proprietary) cellular models. This grade ensures reliability and reproducibility for your research applications.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
C23H27N3O4
10 mg/ml in DMSO
300 nM - 10 µM
Negative (tested using EndotoxDetect™ assay)
In vitro Inflammasome cellular assays
Each lot is functionally tested and validated using cellular assays.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:NT-0796
-
Cat code:inh-nt0796
-
Quantity:1 mg
NT-0796 is provided as a translucent film.
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Room temperature
- -20°C
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
Storage:
Caution:
Details
The NLRP3 Inflammasome
The NLRP3 inflammasome is an innate immune sensor that is activated by a two-step process; a first signal (‘priming’) provided mainly by bacterial components or endogenous cytokines involves NF-κB induction, while the second signal provided by a wide array of stimuli including microbial toxins, endogenous molecules or crystalline substances and leads to inflammasome assembly and activation [1, 2]. This triggers inflammasome multimerization and caspase-1 activation with the subsequent cleavage of interleukin-1β (IL-1β)/IL-18 and the pore-forming protein Gasdermin D (GSDMD) into their active forms. Additionally, the activation of the inflammasome also leads to alarmin secretion and pyroptosis, a form of immunogenic cell death.
1. Swanson K.V. et al., 2019. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19:477.
2. Groslambert M. & Py B. 2018. Spotlight on the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J. Inflamm. Res. 11:359.
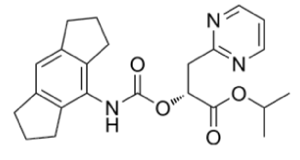
Chemical structure of NT-0796
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Validation Data Sheet
Technical Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?






