Recombinant human BAFF
-
Cat.code:
rcyc-hbaffNEW
- Documents
ABOUT
Human BAFF protein - Mammalian cell-expressed, tag-free, carrier-free
Recombinant human BAFF is a high-quality and biologically active cytokine, validated using proprietary BAFF-R, BCMA, and TACI reporter cells. This member of the TNF superfamily is produced in CHO cells to ensure protein glycosylation and bona fide 3D structure.
Recombinant human BAFF can be used together with HEK-Blue™ BAFF-R, HEK-Blue™ BCMA, or HEK-Blue™ TACI cells for the screening of inhibitory molecules, such as Belimumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting BAFF (see figures).
Key features
- Each lot is validated using HEK-Blue™ BCMA cells
- Endotoxin ≤ 0.001 EU/µg
- 0.22 µm sterile-filtered
Applications
- Standard for BAFF detection and quantification assays
- Screening and release assays for antibodies blocking BAFF signaling
- Screening and release assays for engineered BAFF
B-cell activation factor (BAFF), also called TNFSF13B or BLyS, is a cytokine from the tumor necrosis factor superfamily. Together with A proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL, aka TNFSF13), BAFF plays a prominent role in B cell differentiation, proliferation, survival, and functional responses.
All InvivoGen products are for internal research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
InvivoGen also offers
Learn more
Read our review: The BAFF/APRIL axis in autoimmunity & blood cancers
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
Q9Y275
100 μg/ml in water
Phosphate buffer saline (pH 7.4), 5% saccharose
The absence of bacterial contamination (e.g. lipoproteins and endotoxins) has been confirmed using HEK-Blue™ TLR2 and HEK‑Blue™ TLR4 cells.
Cellular assays (tested), ELISA
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:Recombinant human BAFF
-
Cat code:rcyc-hbaff
-
Quantity:20 µg
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Room temperature
- -20°C
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
Storage:
Caution:
Details
BAFF background
B-cell activation factor (BAFF), also known as TNFSF13B or BLyS, is a cytokine belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. It is a homotrimeric transmembrane protein that is proteolytically cleaved to produce soluble forms [1]. Together with A proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL, aka TNFSF13), BAFF plays a prominent role in B cell differentiation, proliferation, survival, and functional responses.
BAFF is mainly produced by hematopoietic cells, including dendritic cells, monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, T cells, and activated B cells. Recently, non-hematopoietic cells, including astrocytes, osteoclasts, or epithelial cells [1].
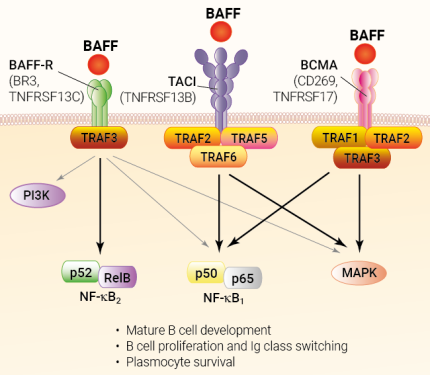
BAFF binds specifically to BAFF-R (TNFRSF13C) and shares two other receptors with APRIL, namely BCMA (B-cell maturation antigen, TNFRSF17) and TACI (transmembrane activator and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor, TNFRSF13B) [1]. Expression levels of BAFF-R, TACI, and BCMA vary with the B cell developmental and maturation stages. This dynamic receptor expression also applies to other cell types, including T cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells.
Each receptor signals through specific pathways [2]:
- BAFF-R:
The best-described signal transduction from BAFF-R is the non-canonical NF-κB (aka NF-κB2) pathway, which leads to the downstream assembly of NF-κB (p52/RelB) transcription factor [2-4]. BAFF-R signaling also activates PI3-kinases, ERK1/2 MAP kinases, and the IKK2-dependent canonical NF-κB (aka NF-κB1) pathway, although the mechanisms by which it does so are unclear [3, 4]. - BCMA:
Upon ligand binding, BCMA recruits TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3, allowing the activation of the canonical NF-κB (aka NF-κB1) and p38 and JNK MAP kinase pathways. These pathways have been described to lead to the downstream assembly of NF-κB (p50/p65) and Elk-1 transcription factors [4, 5]. - TACI:
Upon ligand binding, TACI recruits TRAF2, TRAF5, and TRAF6, allowing the activation of the canonical NF-κB (aka NF-κB1) and JNK MAP kinase pathways. Each pathway leads to the downstream assembly of transcription factors, including NF-κB (p50/p65) and AP1 [4, 6].
The BAFF/APRIL axis in B cells
The BAFF/APRIL system has been extensively described in B cells, in which BAFF and APRIL exert complementary functions.
Immature B cells express high levels of BAFF-R. BAFF/BAFF-R signaling contributes to the transition of immature B cells into mature B cells and promotes the expression of survival genes. Upon antigen activation, mature B cells downregulate the expression of BAFF-R and upregulate BCMA and TACI. Immunoglobulin (Ig) isotype class switching and differentiation into plasmablasts is mediated by BAFF/BAFF-R, BAFF/TACI, and APRIL/TACI signaling. Plasmablasts are proliferating cells that produce large amounts of antibodies to sustain the immune response. Eventually, plasmablasts stop proliferating and become long-lived plasma cells/memory B cells. At this stage, BAFF/APRIL signaling through BCMA and TACI is crucial for the survival of memory B cells.
References:
1. Ullah M.A. & Mackay F., 2023. The BAFF/APRIL system in cancer. Cancers. 15:1791.
2. Balasubramaniam, M. & Mokhtar, A.M.A., 2024. Past and present discovery of the BAFF/APRIL system – A bibliometric study from 1999 to 2023. Cell Signal. 120:111201.
3. Schweighoffer, E., & Tybulewicz, V.L.J., 2018. Signalling for B cell survival. Curr Op Cell Biol. 51:8-14.
4. Schweighoffer, E., & Tybulewicz, V.L.J., 2021. BAFF signaling in health and disease. Curr Op Immunol. 71:124-131.
5. Hatzoglou, A. et al., 2000. TNF receptor family member BCMA (B Cell Maturation) associates with TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 and activates NF-kB, Elk-1, c-Jun N Terminal Kinase, and p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. J Immunol. 165:1322-1330.
6. Xia, X.Z., et al., 2000. TACI is a TRAF-interacting receptor for TALL-1, a tumor necrosis factor family member involved in B cell regulation. J Exp Med. 192(1):137-143.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?