Anti-mMincle-mIgG2a
-
Cat.code:
mab10-mmcl
- Documents
ABOUT
Recombinant anti-mouse Mincle neutralizing and detection antibody
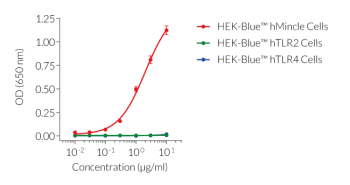
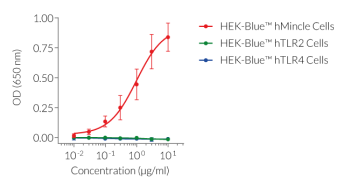
Anti-mMincle-mIgG2a is a monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting mouse Mincle. This antibody was screened for neutralization activity and flow cytometry (see figure).
Anti-mMincle-mIgG2a was previously extracted from hybridoma cells (clone 6G5). It is now expressed and produced in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, ensuring reliability and lot-to-lot reproducibility.
This antibody can be used together with HEK-Blue™ mMincle Cells for screening and neutralization assays to block Mincle signaling in response to stimulation by Mincle ligands.
Key features
- Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
- The complete sequence of the antibody construct has been verified.
- The absence of endotoxins is determined by the EndotoxDetect™ assay.
Macrophage-inducible C-type lectin (Mincle) is a C-type lectin receptor encoded by the C-type lectin domain family 4 member E (CLEC4E) gene. This receptor has emerged as an important player in innate immunity. It recognizes a variety of exogenous and endogenous stimuli, such as mycobacteria, some fungi, and necrotic cells [1, 2].
The hybridoma-derived Anti-mMincle-IgG (mabg-mmcl-2) antibody has been replaced by Anti-mMincle-mIgG2a (mab10-mmcl), which is produced by recombinant technology and purified from CHO cells.
References:
1. Yamasaki S. et al., 2009. C-type lectin Mincle is an activating receptor for pathogenic fungus, Malassezia. PNAS 106(6): 1897–1902
2. Brown G.D., 2008. Sensing necrosis with Mincle. Nature Immunol. 9:1099-1100.
All products are for research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
Mincle, CLEC4E
Mouse
Neutralization assay (tested), flow cytometry (tested)
Sodium phosphate buffer with glycine, saccharose, and stabilizing agents
Negative (tested using EndotoxDetect™ assay)
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:Anti-mMincle-mIgG2a
-
Cat code:mab10-mmcl
-
Quantity:100 µg
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Room temperature
- -20 °C
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
Storage:
Caution:
Details
Mincle is a member of the C-type lectin receptor (CLR) family. Mincle recognizes a variety of exogenous and endogenous stimuli, such as mycobacteria, certain fungi, and necrotic cells [1, 2]. Exogenous ligands for Mincle include fungal α-mannose, and the mycobacterial glycolipid, trehalose-6’6’-dimycolate (TDM), also known as cord factor, the immunostimulatory component of Mycobacterium tuberculosis [3].
Mincle also binds trehalose-6,6-dibehenate (TDB), which is a synthetic analog of TDM. Furthermore, Mincle senses damaged cells by recognizing endogenous damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) [4]. Upon ligand recognition, Mincle interacts with the Fc receptor common γ-chain (FcRγ), which triggers intracellular signaling through Syk, leading to CARD9-dependent NF-κB activation. Syk also induces the mobilization of intracellular calcium (Ca2+) and the activation of the calcineurin-NFAT pathway.
References:
1. Yamasaki S. et al., 2009. C-type lectin Mincle is an activating receptor for pathogenic fungus, Malassezia. PNAS 106(6): 1897–1902.
2. Brown GD. 2008. Sensing necrosis with Mincle. Nature Immunol. 9:1099-1100.
3. Ishikawa E. et al., 2009. Direct recognition of the mycobacterial glycolipid, trehalose dimycolate, by C-type lectin Mincle. J Exp Med. 206(13):2879-88.
4. Yamasaki S. et al., 2008. Mincle is an ITAM-coupled activating receptor that senses damaged cells. Nat Immunol. 9(10):1179-88.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?