THP1-defCASP1 Cells
-
Cat.code:
thp-dcasp1
- Documents
ABOUT
Human monocytes with reduced Caspase-1 activity
Caspase-1 (CASP1), also known as IL-1 converting enzyme (ICE), plays a crucial role in the control of inflammation. Its activity is regulated by a multi-protein complex known as the inflammasome. Upon activation, caspase-1 processes interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18, and Gasdermin-D, promoting inflammation and pyroptosis, a form of cell death [1].
THP1-def cells are derived from THP-1 human monocytic cells. These are the most commonly used model cell line for the study of inflammasome activation as they express high levels of NLRP3, ASC and pro-caspase-1.
THP1-defCASP1 cells are highly deficient for caspase-1 activity (~7 fold reduction). They produce significantly less IL-1β in response to stimuli that activate the inflammasomes, such as ATP, MSU, and chitosan ultrapure (NLRP3 inflammasome) or transfected poly(dA:dT) (AIM2 inflammasome) when compared to the parental cell line THP1-Null. THP1-defCASP1 cells, together with the control cell line THP1-Null, allow to determine if a compound is an inflammasome inducer. The production of IL-1β can be detected using HEK-Blue IL-1β reporter cell line.
Features of THP1-defCASP1 cells:
- Generated from the parental cell line THP1-Null
- Verified knockdown of the CASP1 gene (RT-qPCR)
- Significantly reduced mature IL-1β secretion upon activation of the CASP1
![]() Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Download our Practical guide on Inflammasomes
Reference
1. Man S.M. & Kanneganti T.D., 2016. Converging roles of caspases in inflammasome activation, cell death and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16(1):7-21
Disclaimer: These cells are for internal research use only and are covered by a Limited Use License (See Terms and Conditions). Additional rights may be available.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
Inflammasome activation cellular assays
Complete RPMI 1640 (see TDS)
Verified using Plasmotest™
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:THP1-defCASP1 Cells
-
Cat code:thp-dcasp1
-
Quantity:3-7 x 10^6 cells
- 1 ml of Hygromycin B Gold (100 mg/ml)
- 1 ml of Normocin™ (50 mg/ml)
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Dry ice
- Liquid nitrogen vapor
- Upon receipt, store immediately in liquid nitrogen vapor. Do not store cell vials at -80°C.
Storage:
Caution:
Details
Caspase-1 in inflammmasome responses:
Rapid responses to infections and tissue damages are largely mediated by the inflammasomes. The formation of these cytosolic signaling platforms occurs according to a consensual two-step model. The priming step induces the transcription of pro-IL-1β. The activation step triggers the multimerization of the activated inflammasome sensor with the ASC adaptor and pro-caspase-1. This assembly permits caspase-1 self-activation, which in turn induces the maturation of IL-1β and IL-18 cytokines. Activated caspase-1 also cleaves the N-terminal fragment of gasdermin D (GSDMD), which accumulates to form pores at the cell membrane. These pores allow the unconventional secretion of IL-1β and IL-18, and in the absence of membrane repair, their accumulation leads to pyroptosis.
Application
THP1-defCASP1 cells are designed to study the signals involved in inflammasome activation.
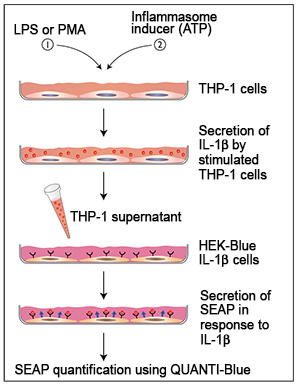
To become susceptible to inflammasome inducers, these cells must be induced by stimuli commonly used for induction in model systems, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and phorbol 12-myristate acetate (PMA). Stimulation by LPS or differentiation with PMA induces the production of pro-IL-1β, the immature form of IL-1β. Subsequent stimulation with inflammasome inducers, such as ATP and alum crystals, leads to caspase-1 activation and IL-1β maturation and secretion. Mature IL-1β can be detected by Western blot, ELISA, or a cell-based assay.
InvivoGen has developed a new method to detect bioactive IL-1β, based on HEK293 cells specifically engineered to selectively respond to IL-1β, named HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells. These cells feature the SEAP (secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase) reporter gene under the control of an NF-kB-inducible promoter. They naturally express the IL-1β receptor (IL-1R), and all the proteins involved in the MyD88-dependent IL-1R signaling pathway that leads to NF-kB activation. Thus upon IL-1β binding to IL-1R, a signaling cascade is initiated triggering NF-kB activation and the subsequent production of SEAP. Detection of SEAP in the supernatant of HEK-Blue™ IL-1β cells can be readily assessed using QUANTI-Blue™, a SEAP detection medium. QUANTI-Blue™ turns blue in the presence of SEAP which can be easily quantified using a spectrophotometer.
Detection of IL-1β in THP-1 supernatants
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?




