FICZ
-
AhR agonist
-
Cat.code:
tlrl-ficz
- Documents
ABOUT
Tryptophan-derived agonist of AhR
FICZ (6-Formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole) is a highly potent ligand of the cytosolic aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) transcription factor.
The presence of FICZ-derived metabolites in human urine points FICZ to be an endogenous AhR agonist, but which requires diet-derived tryptophan (Trp) amino acid [1]. FICZ synthesis results from Trp conversion upon UV-dependent photo-oxidation or H2O2-mediated oxidative stress [2,3].
InvivoGen's FICZ is a high-quality product (>95% purity) and is guaranteed free of bacterial contamination. Each lot of FICZ is functionally tested in cellular assays using HepG2-Lucia™ AhR and HT29-Lucia™ AhR reporter cells.
CH-223191, an AhR antagonist is also available.
![]() Read our review on AhR's key role in the intestinal microbiota and immunity.
Read our review on AhR's key role in the intestinal microbiota and immunity.
References:
1. Wincent E. et al., 2009. The suggested physiologic aryl hydrocarbon receptor activator and cytochrome P4501 substrate 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole is present in humans. J. Biol. Chem. 284:2690-96.
2. Rannug A. et al., 1987. Certain photooxidized derivatives of tryptophan bind with very high affinity to the Ah receptor and are likely to be endogenous signal substances. J. Biol. Chem. 262:15422-27.
3. Smirnova A. et al., 2018. Evidence for new light-independent pathways for generation of the endogenous aryl hydorcarbon receptor agonist FICZ. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 29:75-86.
All InvivoGen products are for internal research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
C19H12N2O
50 ng/ml (0.18 µM) to 5 μg/ml (18 μM)
10 mg/ml (37.17 mM) in DMSO
AhR activation using HepG2-Lucia™ AhR and HT29-Lucia™ AhR reporter cellular assays
Each lot is functionally tested and validated.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:FICZ
-
Cat code:tlrl-ficz
-
Quantity:1 mg
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Room temperature
- -20°C
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
Storage:
Caution:
Details
FICZ chemical structure
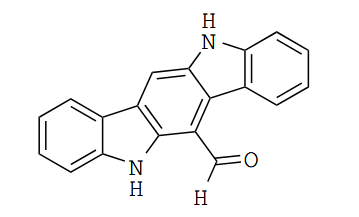
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcriptional factor able to sense a wide range of structurally different exogenous and endogenous molecules.
AhR ligands vary in their structure, and their binding affinity can significantly differ between mouse and human AhR [1]. AhR agonists have been found to arise from xenobiotics such as pollutants, and indoles mainly derived from tryptophan metabolism occurring in the stomach and in the gut, as well as in other organs upon photo-oxidation or oxidative stress. The prototypic high-affinity AhR agonist, the xenobiotic 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), displays a 10-fold higher affinity for mouse AhR compared to human AhR. Conversely, dietary-derived indole metabolites have a better affinity for human AhR; a possible consequence of evolution [1-3].
References:
1. Lamas B. et al., 2018. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and intestinal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 11(4):1024-38.
2. Murray I.A. et al., 2017. Ligand activation of the Ah receptor contributes to gastrointestinal homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2:15-23.
3. Hubbard T.D. et al., 2015. Indole and tryptophan metabolism: endogenous and dietary routes to Ah receptor activation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 43:1522-35.
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?





