Cytokines / Innate immunity
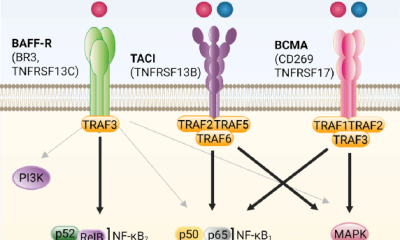
The BAFF (B cell activating factor) and APRIL (A Proliferation-Inducing Ligand) cytokines are...
Innate immunity / PRR

C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) comprise a large family of receptors that bind to carbohydrates in a...
Inflammasome / Innate immunity

The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) family of proteins is involved in...
Innate immunity / PRR

The cytosolic NOD-Like Receptors (NLRs, also known as CATERPILLERs, NODs or NALP/PAN/PYPAFs) are...
Innate immunity / PRR

Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) play a critical role in the early innate immune response to invading...
Vaccination

Adjuvants are essential for enhancing and directing the adaptative immune response to vaccine...
Products

RNA interference (RNAi) is one of the most exciting discoveries of the past decade in functional...
Products

Review of the effect of CpG dinucleotide on the immune response and the gene silencing of gene...
Innate immunity

Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a pivotal role in the initiation of prompt innate immune defenses...
Innate immunity / PRR

RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) constitute a family of cytoplasmic RNA helicases that are critical for...
Innate immunity / PRR

Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are the best studied pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and their...
Innate immunity / PRR / STING

Cytosolic DNA is well-known to induce the production of type I interferons (IFNs) through the STING...
COVID-19

The global vaccine effort in response to the COVID-19 pandemic is unprecedented in terms of both...
Innate immunity / Inflammasome

Regulated cell death (RCD) is a lethal process taking place in the context of stressful stimuli (e.g...
COVID-19

Learn more about the growing evidence that re-infection by SARS-CoV-2 can occur, with protective...
COVID-19

Currently, there is very limited knowledge of the host immune response to SARS-CoV-2. However, based...

