LPS-RS
-
Cat.code:
tlrl-rslps
- Documents
ABOUT
LPS from Rhodobacter sphaeroides
Lipopolysaccharide from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides (LPS-RS) is a potent antagonist of toxic hexa-acylated LPS in human and murine cells [1]. It also prevents LPS-induced shock in mice [1]. Complete competitive inhibition of LPS activity is possible at a 100-fold excess of the antagonist. LPS-RS does not induce TLR4 signaling but is detected by the LAL standard endotoxin detection assay.
Mode of action
LPS-RS is penta-acylated, and like other under-acylated LPS, appears to use at least two distinct mechanisms to block LPS-dependent activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). The primary mechanism consists of direct competition between under-acylated LPS and hexa-acylated LPS for the same binding site on MD-2, while the secondary mechanism involves the ability of under-acylated LPS-MD-2 complexes to inhibit the TLR4 agonist activity of hexa-acylated LPS-MD-2 complexes [2-5].
Key features of LPS-RS Standard
- LPS preparation extracted by a phenol-water mixture
- Inhibits TLR4 activity
- Activates TLR2, as it contains other bacterial components, such as lipoproteins
- Detectable using the LAL assay
Key features of LPS-RS Ultrapure
- LPS extracted by successive enzymatic hydrolysis steps (phenol-TEA-DOC extraction protocol [6])
- Inhibits TLR4 activity
- Does not activate TLR2, as contaminating lipoproteins have been removed
- Detectable using the LAL assay
References:
1. Qureshi, N. et al., 1999. Nontoxic RsDPLA as a potent antagonist of toxic lipopolysaccharide. p. 687-98. In: Brade H., Opal S. M., Vogel S. N., and Morrison D. C., eds. Endotoxin in Health and Disease. Marcel Dekker, New York.
2. Coats SR. et al., 2005. MD-2 mediates the ability of tetra-acylated and penta-acylated lipopolysaccharides to antagonize Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide at the TLR4 signaling complex. J Immunol. 175(7):4490-8.
3. Teghanemt A. et al., 2005. Molecular basis of reduced potency of underacylated endotoxins. J Immunol. 175(7):4669-76.
4. Visintin A. et al., 2005. Pharmacological inhibition of endotoxin responses is achieved by targeting the TLR4 coreceptor, MD-2. J Immunol. 175(10):6465-72.
5. Saitoh S. et al., 2004. Lipid A antagonist, lipid IVa, is distinct from lipid A in interaction with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-MD-2 and ligand-induced TLR4 oligomerization. Int Immunol. 16(7):961-9.
6. Hirschfeld M. et al., 2000. Cutting edge: repurification of lipopolysaccharide eliminates signaling through both human and murine toll-like receptor 2. J Immunol. 165(2):618-22.
All InvivoGen products are for internal research use only, and not for human or veterinary use.
More information
Learn more about TLR4 and its co-receptors
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
TLR4
10 ng/ml - 10 µg/ml
5 mg/ml in water
Inhibition of TLR4 cellular responses
TLR4 inhibition
Sepsis research
Each lot is functionally tested and validated using cellular assays.
CONTENTS
Contents
-
Product:LPS-RS
-
Cat code:tlrl-rslps
-
Quantity:5 mg
1.5 ml endotoxin-free water
Shipping & Storage
- Shipping method: Room temperature
- -20 °C
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
Storage:
Caution:
Details
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) primarily recognizes and is activated by a core component of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, lipopolysaccharide (LPS). TLR4 requires interaction with a number of co-receptors including LPS-binding protein (LBP), CD14 and, myeloid differentiation protein 2 (MD-2) to bind to LPS and induce a signaling cascade. Ultimately, this leads to the activation of NF-κB and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
LPS consists of a polysaccharide region that is anchored in the outer bacterial membrane by a specific carbohydrate-lipid moiety termed lipid A (also known as endotoxin). It is the lipid A region that is responsible for the immunostimulatory activity of LPS.
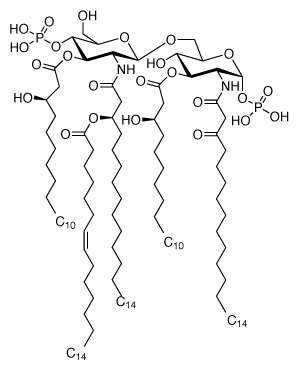
Variation in lipid A, specifically the number of fatty acyl chains, among diverse bacterial species cause a vast difference in the biological activity of LPS.
There are two major variations of lipid A:
- Hexa-acylated (6 fatty acid chains): a highly active agonist of TLR4 and is found commonly on pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp.
- Under-acylated (4-5 fatty acid chains): induces a significantly lower host response and can be an antagonist of TLR4, by inhibiting, in a dose-dependent manner, the strong endotoxic response triggered by hexa-acylated LPS.
Structure of lipid A from Rhodobacter sphaeroides:
DOCUMENTS
Documents
Technical Data Sheet
Safety Data Sheet
Validation Data Sheet
Certificate of analysis
Need a CoA ?








