The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcriptional factor expressed by many cell types, particularly in barrier tissues, such as the gastro-intestinal tract.
AhR sensing of environmental pollutants and dietary-derived compounds contributes to the intestinal homeostasis between the host and gut microbiota.
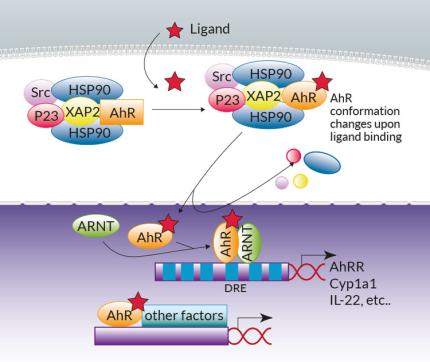
AhR canonical genomic signaling has been extensively reviewed [1,2]. Briefly, in the absence of ligands, AhR resides in the cytoplasm within a Hsp90:XAP2:p23:Src chaperone protein complex. Upon ligand binding, the complex translocates into the nucleus, the chaperones are released, and AhR heterodimerizes with AhR nuclear translocator (ARNT). The AhR:ligand:ARNT trimer binds to dioxin response elements (DREs) in the upstream regulatory regions of AhR target genes, which include the cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase Cyp1a1, the AhR repressor (AhRR), and the IL-22 interleukin.
Of note, non-canonical AhR signaling pathways have also been reported, either at the genomic level through association with other transcription factors (e.g. NF-κB), or at the non-genomic level (e.g. through the release of the Src kinase) [2,3].
InvivoGen provides two AhR reporter cell lines allowing the study of AhR canonical genomic signaling upon incubation with a wide range of agonists such as xenobiotics, synthetic dietary-derived indole products, or endogenous AhR agonists from human samples.
- HT29-Lucia™ AhR Cells are engineered from the human HT29 colon carcinoma and are highly relevant for studying intestinal microbiota-related ligands for AhR.
- HepG2-Lucia™ AhR Cells are engineered from the human HepG2 hepatoma and are particularly suitable for the detection/screening of AhR ligands in food or environmental samples.
![]() Read our review on AhR’s key role in the intestinal microbiota and immunity
Read our review on AhR’s key role in the intestinal microbiota and immunity
References:
1. Stockinger B. et al., 2014. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: multitasking in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 32:403-32.
2. Lamas B. et al., 2018. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and intestinal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 11(4):1024-38.
3. Gutiérrez-Vasquez C. et al., 2018. Regulation of the immune response by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Immunity. 48:19-33.